
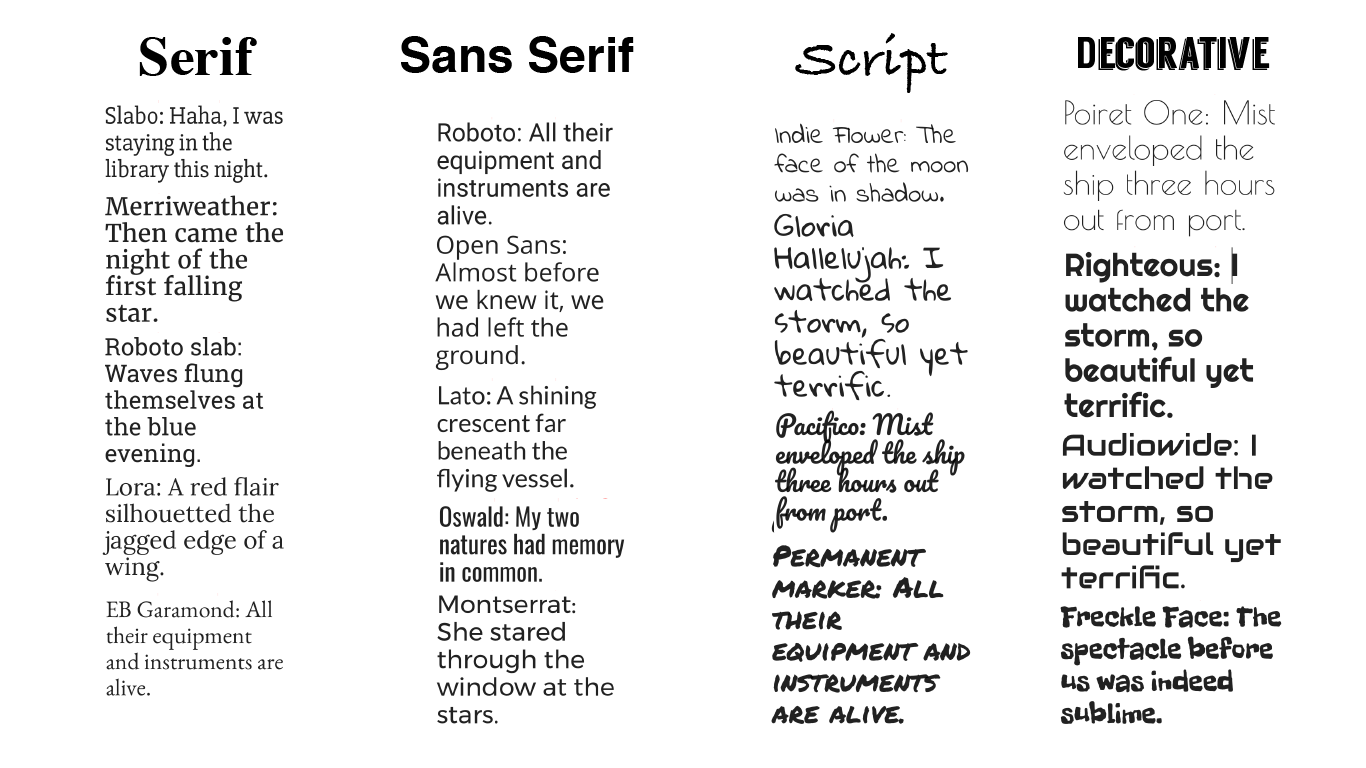
This property specifies the size of the font. Anytime a font's name is more than one word, it must be in quotation marks. Note that in the above example, "Times New Roman" appears in quotation marks, whereas the other fonts don't. This is the fallback font, to be used if none of the preferred fonts are available. The last font in the list should always be one of the five generic font families, described above. If they don't, the browser will try to display the next font in the list. If the user has the first font in the list installed on their computer, their browser will display that font. The value of font-family is a list of preferred fonts, separated by a comma, as in these example:įont-family: "Times New Roman", Times, serif This property specifies the font of an element. Here are a few of the most common: font-family Typography on the Web involves the interplay between various properties in CSS. Depending on the message or feeling you're trying to communicate, they might be suitable for short sections of text, such as headings or subheadings. These fonts are more difficult to read and should be used sparingly. What about cursive, fantasy, and monospace? However, it's possible to attain this look with certain serif fonts as well.įor page titles, headings and sub-headings, a serif font is sometimes a better choice, because they can be perceived as more stately and grand, which helps to contribute to how readers perceive the hierarchy of the page. Generally the best choice for attaining this uncluttered, flowing, easy-to-read look is sans-serif. For the body of a web page, it's important to choose a font that is not too cluttered and that flows gracefully from letter to letter without too much space between letters. The bottom line: There are many variables affecting readability of text, not just font family alone. There are dozens of studies favoring both font families. There has been extensive research on which of these font families, serif or sans-serif, is easier to read. These fonts are simple and straightforward. Sans-serif fonts do not have serifs ("sans" is French for "without"). Serif fonts have been used for centuries in printed books, magazines and newspapers. They can look like small feet, caps, tails, flags or dots. Serif fonts have small lines or strokes that extend from the ends of characters. In CSS (and in typography in general) there are five basic types, or families, of fonts: serif, sans serif, cursive, fantasy, and monospace. you will be able to define the typography of your site by setting the font-family, font-size, font-weight, line-height, text-align, and letter-spacing properties in CSS.įont Families: Serif, Sans-serif, and others.you will be able to make informed decisions about which font families to use on a website, based in part on the likelihood that these fonts will be installed on users' computers.you will be able to identify whether a font is serif, sans-serif, or another font family.You will also learn some strategies for selecting a font family.
In this lesson you will learn some of the specific CSS properties that are used to define typography on web pages, and will apply these properties to your portfolio website. Let's take a look at an example of a document with unprofessional fonts.UNIT 3 > MODULE 3 Lesson 2: Applying Typography in CSS Overview


If a font is distracting or undermines your message in any way, it needs to be changed. This will help make it look more cohesive and professional.Ī font should also never take the focus away from your content, so avoid fonts that are goofy or decorative. One way to keep it simple is to only use one or two fonts per document.
FONTS MEANING HOW TO
Keeping it simpleĪs we discussed in our lesson on how to format a business document, your writing is most effective when the formatting is simple. Increasing the heading size to a 14-point or 16-point font is usually more than enough to make your heading stand out. Headings, on the other hand, can be larger than a 12-point font if you need to add emphasis. If you can't decide between sizes, a 12-point font is usually the reliable choice because it's incredibly common in the business world. This means your body text should be a 10-point to a 12-point font, depending on the look you want and your company's preferred style. Font sizeĪn effective font size is big enough to easily read but doesn't take up too much space. Ultimately, you should choose the font that best fits your message and desired look. However, others believe that either font type can be legible no matter where you use it. Many typography experts believe serif fonts are more legible in print and sans serif fonts are easier to read on computer screens.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
